
What is a lab grown diamond?
Whether mined from the earth or grown in a lab, diamond is crystallized carbon. It is the hardest of all minerals, but can chip or cleave if impacted with enough force. What makes diamonds so attractive is their high dispersion and refractive properties, which reflect, refract, and split the light into spectral colours. This gives diamonds their distinctive sparkle and fire.
Lab grown diamonds have the exact same chemical, physical, and optical properties of a mined diamond, just for a fraction of the cost. Additionally, they are more sustainable, and are more traceable than mined diamonds.

How are diamonds valued?
Generally speaking, diamonds are priced using a price per carat (1 carat = 0.2 grams). The more rare and in demand the diamond is, the higher price per carat.
Larger diamonds, high colour or clarity, and rare fancy colours will command the highest price per carat.
For lab grown diamonds, the costs to produce the diamond play a larger role in the price per carat.
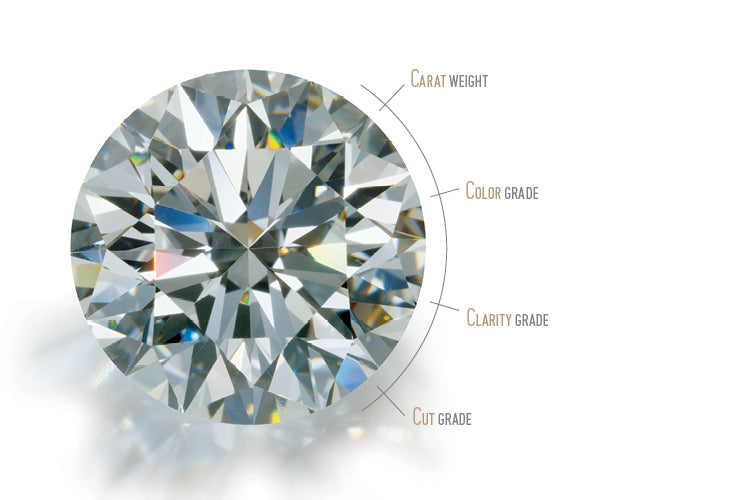

How are diamonds graded?
Diamonds, both mined and lab grown, are graded on the 4C's - carat, colour, clarity, and cut.

Carat
Diamonds are weighed and assigned a carat weight. One carat (denoted at 1ct) is 1/5th of a gram, or 0.2 grams. Generally speaking the larger the diamond, the more it will cost. Note that since carat is a measure of weight, some cuts, such as a cushion cut or emerald cut, will appear smaller than shallower cuts such as a round or oval cut, though they may have the same carat weight.

Colour
Colour is a measure of just that - the diamond's colour. For colourless to slightly tinted diamonds, an alphabetical grading scale is used. D is the brightest and most colourless grade, going down to a faint tint at the Z grade. These are not to be confused with fancy colour diamonds, which are more intense in colour and use a seperate grading system.
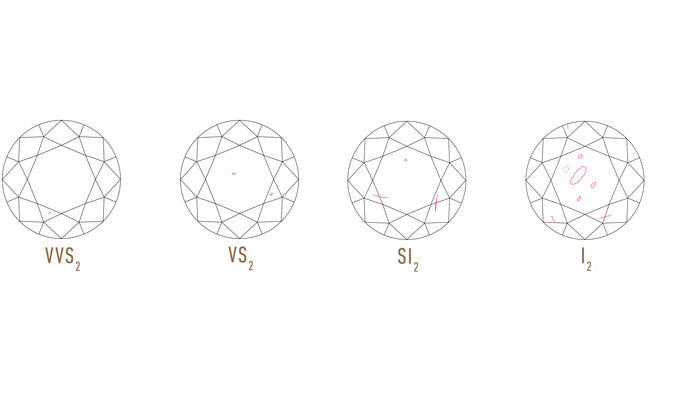
Clarity
Clarity is the measure of the inclusions or imperfections in the diamond. This can include other mineral inclusions, structural defects such as cracks (feather inclusions) or cloudy areas within the diamond. The higher the clarity grade, the higher the value of the diamond.
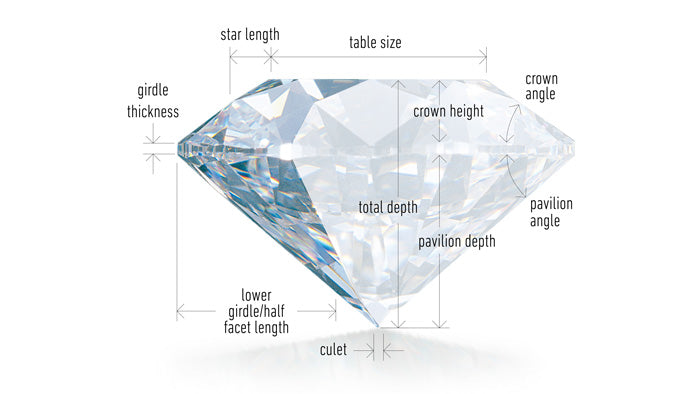
Cut
Not to be confused with the diamond's shape, the cut refers to the craftmanship of the facetting of the diamond. This looks at all of the angles and proportions, as well as the symmetry of the facets and the polish quality, and assigns a cut grade. Regardless of colour and clarity, it is the cut that determines the sparkle and fire of the diamond.